Research Experience
Experimental Investigation on Mechanical and Physical Properties of Sisal Fiber Reinforced Hybrid Composites with Filler Material
Abdullah Al Rafi, Md. Shamim Ali ,Md. Abu Mowazzem Hossain* , Raihan Ahmed Redoy
Jun 2024 – Dec 2024
Abstract
Natural fiber composites have gained prominence due to their sustainability, lightweight properties, biodegrad- ability, and eco-friendliness. Among various natural fibers as reinforcement, sisal fiber is particularly notable because of its low production costs, environmental advantages, and strong mechanical properties, which make it suitable for a variety of applications. This study experimentally investigated the mechanical and physical prop- erties of hybrid composites reinforced with sisal fibers. The composites are fabricated using the hand lay-up technique, incorporating epoxy matrices that are enhanced with sisal fibers treated in a 5 % NaOH solution. The experimental results indicate that the tensile strength and impact strength of the composite reinforced with 30 % treated sisal fiber (TSF) increased by 22.35 % and 18.87 %, respectively, when compared to the composite containing 20 % TSF and 10 % treated wood powder (TWP). This improvement is attributed to enhanced energy absorption and better stress distribution associated with the higher fiber content. Furthermore, the Rockwell hardness of the composite with 30 % TSF is 14.81 % greater than that of the composite with 20 % TSF and 10 % TWP, likely due to improved fiber-matrix adhesion and greater cross-link density. In terms of physical properties, the hydrophilic nature of sisal fiber results in a 16.41 % increase in water absorption capacity for the composite made with 30 % TSF compared to the composite with 20 % TSF and 10 % TWP. These findings highlight the potential of sisal fiber-reinforced composites for various industrial applications, particularly in the context of sustainable material development.
Objective
This study aims to de- velop hybrid composites reinforced with sisal fibers and wood powder fillers, focusing on minimizing void formation that weakens the com- posite. By exploring microstructural bonding mechanisms, it seeks to optimize fiber-matrix adhesion for improved composite efficiency. In addition, this study will evaluate various properties of the developed hybrid composites, such as tensile strength, water absorption, and im- pact resistance, to assess their suitability for real-world applications.
Graphical Representation
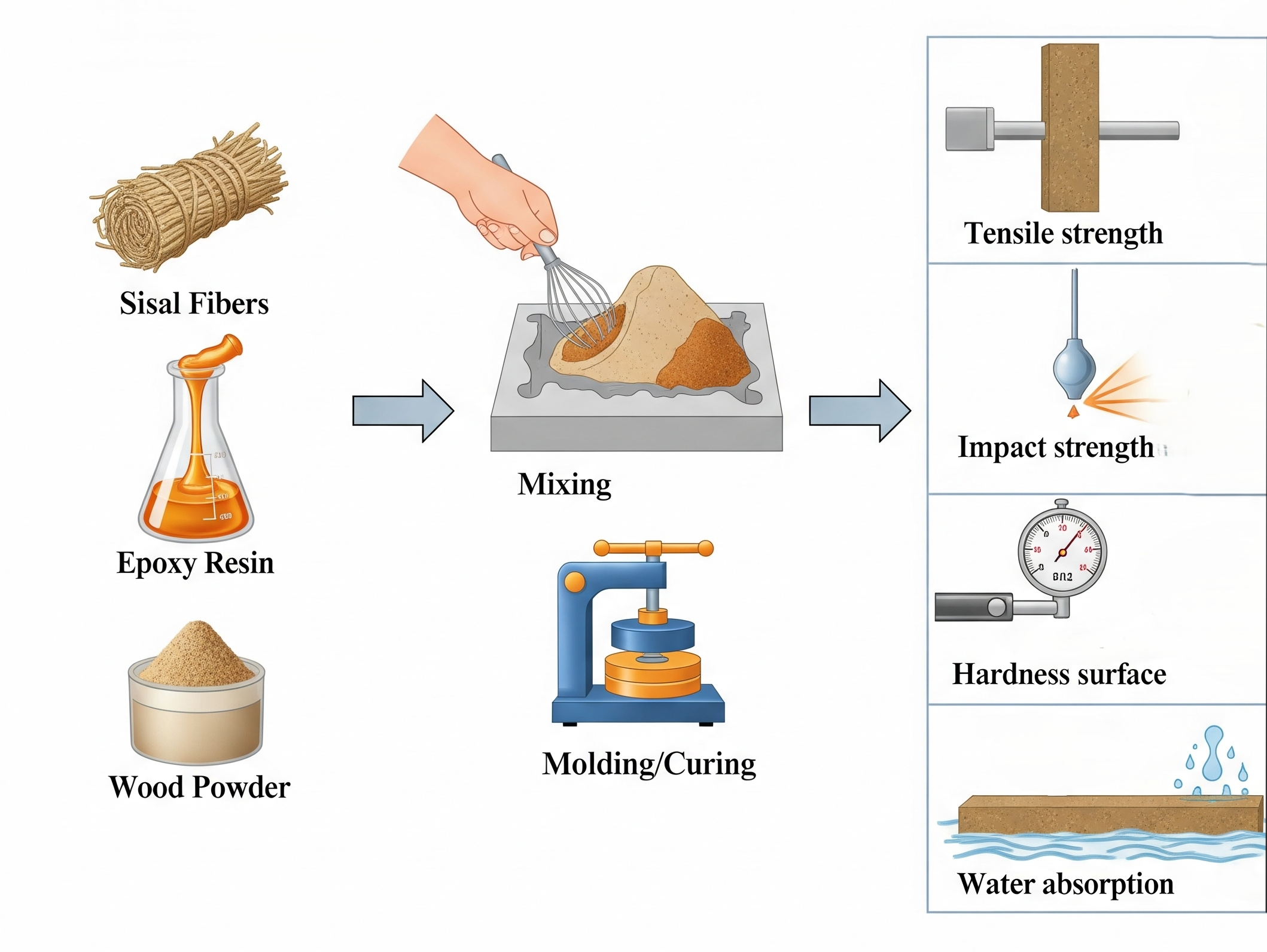
Key Points
- Developed three material samples by varying the percentage of sisal fiber (20%, 25%, 30%) and wood powder (0%, 5%, 10%) using the hand-layup technique.
- Measured the mechanical and physical properties of the sample and compared them with similar types of material.
- Performed Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) test and observed the microstructure of the sample.
