Research Experience
A Comparative Analysis Between Balsa and Pine as a Potential Piezoelectric Material
Zaber Mhamud
Feb 2024 – Jun 2024
Abstract
The continuous necessity of renewable and sustainable energy has driven mankind to think outside the box. Wood has become a potential contender in harnessing electricity by the piezoelectric effect and in the bio-sensor application. This natural composite exhibits great potential in this field due to its cellulose, microfibril, and dipolar regions. So, it has an enormous possibility of efficiently generating electricity in response to mechanical stress or vibration. However, voltage generation in response to stress can change over selected wood samples. This paper exhibits the fabrication process, comparative analysis between selected wood samples and the reason behind the piezoelectricity of those wood samples.
Objective
Being a fairly new research topic, the energy generation and biosensor application using wood doesn’t develop that much. Only the balsa wood is introduced in this field. Here in this study both balsa and pine tree wood have been used as raw materials. The selection criteria of wood is based on lower cell wall thickness. As the target is to make the treated wood spongy as much as possible it is essential to select a wood that has low density and a thin cell wall. The delignification process will take away lignin from the wood sample and hence make it constructed only with cellulose and hemicellulose. That’s why pine and balsa are selected as both have low density and small cell wall thickness.
Graphical Representation
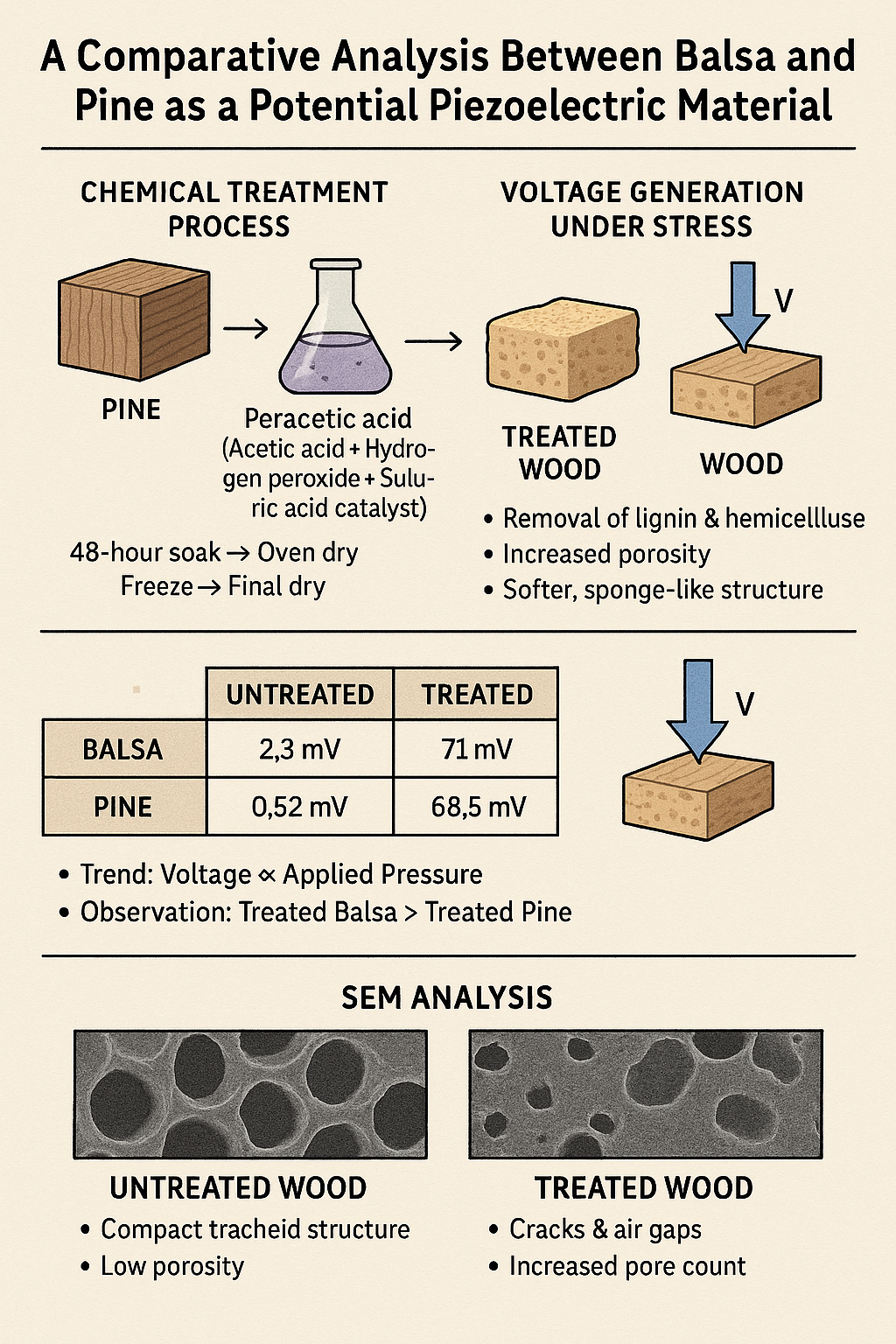
Key Points
- Experimented to enhance the piezoelectric properties of Balsa and Pine.
- Performed Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) analysis to study porosity and microstructure of Balsa and Pine.
- Developed chemically treated Balsa and Pine, and measured the voltage generated by applying stress on it.
